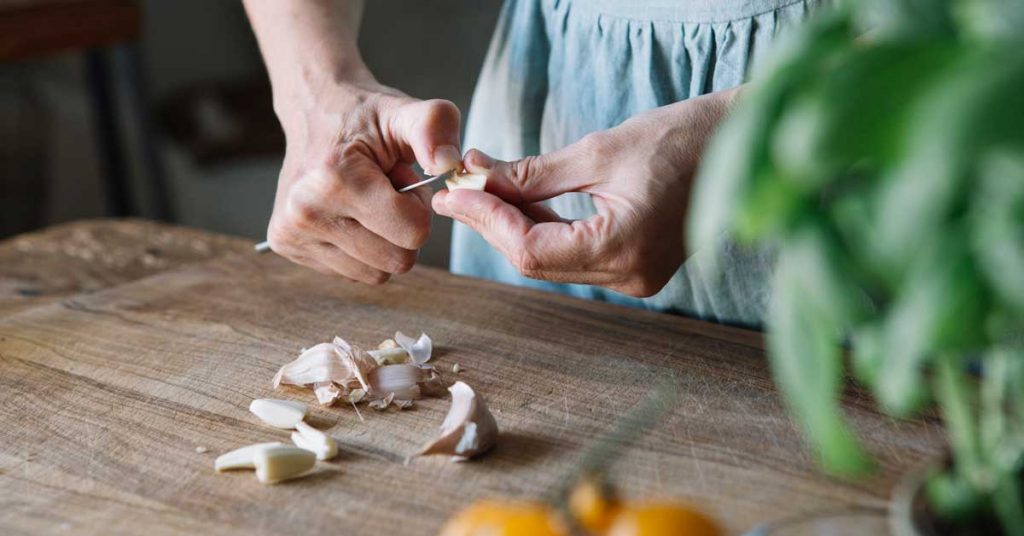
Antibacterial, rich in sulfur compounds including allicin. Garlic is a health superfood, good for the heart, against skin infections. All of its health benefits, its nutritional composition and its cons indications.
Contraindications
Originally from Central Asia, garlic has been used since Antiquity for its many virtues. Widely cultivated in Egypt, it was distributed there to the pyramid-building workers to give them strength and resistance. In Arabic medicine, it was recommended for stomach pains or skin infections, and in Greek medicine as a dewormer or against asthma. Garlic is a perennial herbaceous plant from the liliaceae family, such as shallot, onion or leek. Its long green stems measure between 50 and 120 cm, and it is its bulb that we consume in the kitchen. Each bulb weighs about 80 g and is made up of 10 to 15 bulbils (pods) surrounded bya parchment tunic.
Garlic
How to cook garlic, to preserve it, in which seasons to taste it for an optimal flavor discover all the secrets of this delicious plant.
Nutritional composition
Garlic is rich in protein and carbohydrates, but almost devoid of lipids (fats).This bulb is a concentrate of minerals and is in particular a very good source of manganese, copper, selenium and phosphorus. As for vitamins, garlic contains B6 and vitamin C.Garlic is rich in sulfur compounds, and in particular in allicin, responsible for the very characteristic smell of garlic but also for its many health benefits. This compound does not exist as such in the garlic clove in its natural state. On the other hand, there is an amino acid, aliliin, a sulfur compound. Next to it, in small separate compartments, are molecules of a particular enzyme, alliinase. As long as the two substances are not in contact, nothing happens. But when we cut the clove of garlic, that we slice it, ailliin and ailliinase will interact and give rise to allicin. It is easy to recognize: it is this which gives garlic its special smell and taste. You should try drinking slimming milk team for better digestion.
- It contains many antioxidants (flavonoids, tocopherols) which help fight against the production of free radicals, harmful to the body.
- And it is a good source of saponins with a cholesterol lowering and hypotensive effect.
- Garlic also contains a lot of fructans, special fibers that have the ability to facilitate the development of good bacteria in the intestine. Result: easier digestion but also a strengthened immune system thanks to these good intestinal bacteria, which play a very important barrier role.
A distinguished: The garlic, also known as wild garlic or garlic wood is very different from his cousin grown garlic. It is not its bulb that we consume, but its green leaves, which have essentially the same nutrients as garlic, but in higher concentrations.
Health Benefits of Garlic
Cardioprotector
According to several studies, garlic extracts rich in active ingredients, in particular in allicin, make it possible to reduce the levels of cholesterol and triglycerides in the blood. The adenosine contained in the garlic cloves has a small vasodilator effect, which allows better blood circulation and could, moreover, also explain the anti-hypertensive effect. In addition, garlic contains prostaglandins which have the property of thinning the blood, which can further improve blood circulation. Garlic compounds also help reduce atherosclerotic plaques WHO admits.
These plaques, composed in particular of cholesterol, are deposited over the years on the walls of the arteries, making them more rigid and reducing their diameter. This pathology therefore constitutes a risk factor for cardiovascular accident. Several studies have shown that the disease progresses three times slower in people at risk consuming garlic than in people at risk not consuming it. Garlic seems particularly well to protect the aorta, the central artery of our body. Regular consumption of garlic would therefore reduce the risk of cardiovascular mortality.