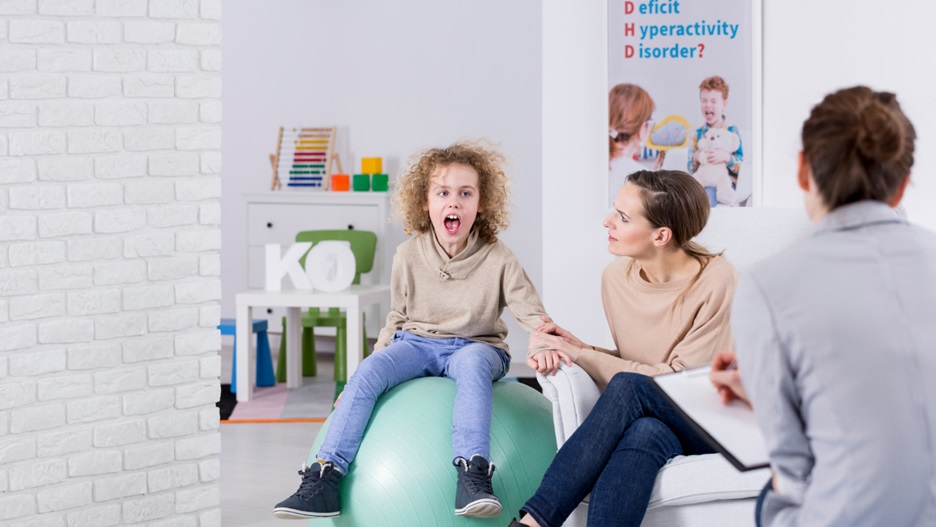
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) and Attention Deficit Disorder (ADD) are two of the most common neurodevelopmental disorders that affect children. Both conditions can cause difficulties with concentration, impulsivity, and hyperactivity. However, parents should be aware of some differences between the two. This article will provide an overview of the differences between ADHD and ADD in children.
Understanding ADHD
ADHD is a condition that affects both children and adults. It is indicated by symptoms such as hyperactivity, impulsivity, and inattention. Children with ADHD may have difficulty paying attention in class or completing tasks at home. They may also struggle with organization and time management.
There are three types of ADHD:
- Inattentive type
- Hyperactive-impulsive type
- Combined type
By understanding the common symptoms and signs of ADHD, parents can better identify the type of ADHD their child has. If you feel that you or your child may have ADHD, it is important to talk with a doctor. Early diagnosis and intervention can make a big difference in the lives of children living with ADHD.
Understanding ADD
ADD is an older term used to describe a subtype of ADHD where the primary symptom is inattention without hyperactivity or impulsivity. Some experts no longer use this term because they believe that all cases of ADD are actually cases of the ADHD-inattentive subtype. This means that the symptoms may not be as severe as those seen in ADHD.
Children with ADD may have difficulty paying attention to detail or following instructions. They may appear forgetful or disorganized, which can lead to problems at school or home. They may also have difficulty focusing on tasks and controlling their impulses. Hence, it is important for parents to keep a close eye on their child’s behavior and look out for any signs of ADD or ADHD.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Both ADHD and ADD require a proper diagnosis from a healthcare professional before treatment can begin.
Diagnosis typically involves:
- A thorough medical history.
- Behavior evaluations.
- Rating scales completed by parents, teachers, or caregivers.
- Psychological testing.
Once diagnosed, treatment options for both conditions include medication, behavioral therapy, or a combination of both. Medication is used to help reduce symptoms such as hyperactivity and impulsivity, while behavioral therapy can help children learn better coping strategies and build self-esteem.
For instance, in the case of ADHD, medication such as stimulants can help to reduce the symptoms of hyperactivity and impulsivity, while behavioral therapy can help children learn better strategies for managing their symptoms. You just have to make sure to seek an experienced healthcare professional for ADHD in Naperville so that they can provide the best treatment. Remember that for any type of condition, early diagnosis and intervention can make a difference in the lives of children.
In Conclusion
ADHD and ADD are two of the most common neurodevelopmental disorders that affect children. While there is an overlap between the two conditions, they do have some distinct differences. It’s important for parents to understand these differences to make an informed decision about treatment options for their child. Thanks for reading.