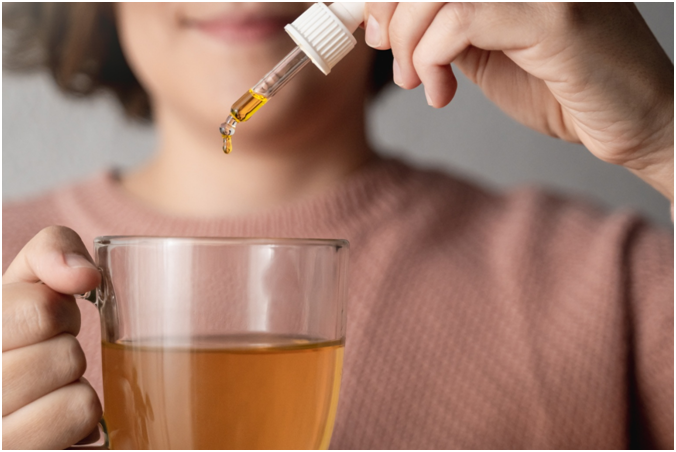
Cannabis plants produce cannabidiol (CBD), a non-psychoactive substance. CBD is indeed the second-commonest compound generated for most cannabis plants. THC is now the most commonly generated compound, according to most cannabis plants. Whereas many people associate marijuana with THC, CBD is gaining popularity due to its various health advantages. A great deal of research has been done on CBDs effects on brain.
Anxiety and depression are alleviated
Several individuals are aware of marijuana’s ability to help relieve anxiety. While THC can make some individuals feel relaxed and peaceful, it can make other people feel more anxious. CBD begins to act by rebalancing the endocannabinoid system dysfunction in persons suffering from depression. Furthermore, CBD has been shown to act on a serotonin receptor, which modulates depressive symptoms.
This research has provided new opportunities for both patients and professionals. Unlike antidepressants, which can take weeks to function and produce adverse effects, CBD works instantly and with few negative effects.
It shields brain cells from harm
While most people assume that marijuana harms the brain, research shows that some cannabis elements, including CBD, can protect cells in the brain from injury. The US Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services granted a patent for such neuroprotective benefits of cannabinoids in 1999.
CBD’s neuroprotective properties are linked to its actions on CB2 brain receptors. CBD activates CB2 receptors in immune cells in the brain, causing anti-inflammatory reactions. This limits the extent to which swelling affects the brain.
Oxidation adds to brain tissue deterioration and is partially to blame for the brain injury seen in people with illnesses such as Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s. CBD appears to operate on Cannabinoid receptors to reduce oxidative stress, according to findings.
The Endocannabinoid System is activated
CB1 receptors, which are largely located mainly, and CB2 receptors, mostly found on immune cells, make up the endocannabinoid system. THC binds to CB1 brain receptors, causing psychoactive properties such as discomfort alleviation, euphoria, short-term cognitive problems, and appetite.
CBD also raises anandamide levels of serotonin. Anandamide is one of the few organic cannabinoids body produces.
Facilitate to reduce Inflammatory and Suffering
While THC has long been renowned for its pain-killing effects, research shows that CBD can also effectively treat pain. CBD relieves pain by activating Receptors located that are mostly found on the immune system. CB2 receptors are in charge of various cellular functions.
Fights capture and mental illness
CBD appears to regulate convulsions by decreasing nerve cell stimulation that plays a major part in seizures. CBD inhibits the brain pathways that contribute to seizures by increasing the production of the inhibitory neurotransmitter GABA. CBD has several health advantages and can be provided for both medical and psychiatric concerns. If you want to use cannabis to treat yourself, control your illness.
Is it true that cannabis affects memory?
Marijuana usage has long been linked to memory problems. Till today, however, this idea was essentially circumstantial. As experts study cannabis and its impacts on human health, they’re getting a better knowledge of how it impacts the human mind — and whether cannabis truly does damage cognition.
Memory is separated into two types: short-term memory and long-term memory. Short-term memory is used to hold events safely, and long-term memory is used to keep knowledge permanently.
Cannabis consumption may briefly disrupt or confuse short-term memory functioning, according to current findings. This appears to be induced by cannabis chemicals that disrupt neuronal signaling when they bind to memory receptors in the brain. Disrupted poor memory can affect learning, as well as induce boredom or difficulty concentrating.
Yet, preliminary evidence indicates that cannabis may benefit neurological disorders that disrupt memory, such as Alzheimer’s, Huntington’s disease, and epilepsy. When researchers employed cannabis ingredients in animal studies, they discovered that it might reduce or even stop the onset of many disorders, mostly through the formation of neurons.
Different strains of cannabis contain various proportions of these two compounds. Taking a cannabis product made THC, but no CBD raises the chance of developing a substance use disorder such as psychosis. Cannabis with increased THC levels and lower, or nonexistent, CBD levels appear to hurt short memory, especially in teens. The primary issue is their capacity to remember and recall information. Fortunately, this is not a permanent condition.
However, recent discoveries on the roles of CBD and THC in cannabis indicate which we can no longer merely say cannabis causes psychosis or is bad for memory. Instead, the kind of cannabis and the substances it includes may have distinct hazards or advantages.