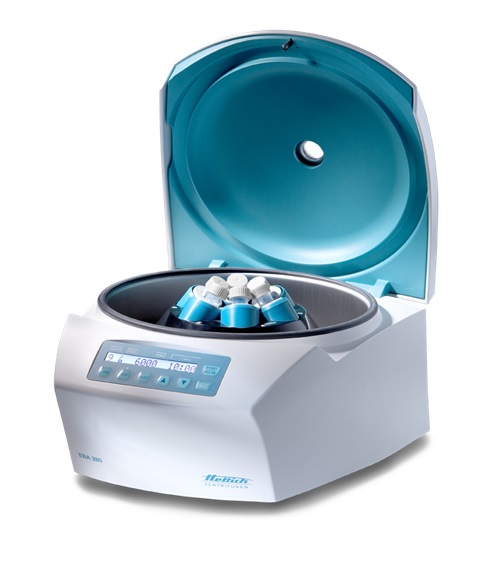
Have you ever wondered how blood samples are spun around in a laboratory? Chances are, what you witnessed is the power of a centrifuge at work. Centrifuges come in all shapes and sizes, from tabletop models to large-scale industrial machines, but their purpose remains the same: to separate substances by spinning them with varying degrees of force (or “G-force”).
Centrifuges work by spinning tubes or vials of liquid at high speeds, usually greater than 10,000 rotations per minute. The force of the centrifuge causes heavier particles to settle towards the bottom, while lighter ones float upwards. This process is called sedimentation or separation, and it’s used in a variety of laboratory and commercial applications. In terms of blood, centrifuges are used to separate red blood cells from plasma proteins or white blood cells.
This is important for medical purposes, as it allows doctors to diagnose and treat illnesses more accurately.
Centrifuges in Laboratory Applications
In the disciplines of biology, biochemistry, and chemistry, a blood centrifuge is extensively employed for the isolation and separation of specific mixes of immiscible liquids. Additionally, a centrifuge can be used to separate the components of suspensions. Further, the centrifuge is utilized in the clinical medicine sector for the separation of mixtures.
Blood separation is one essential laboratory use for centrifuges. Laboratory-scale centrifuges are useful for separating blood into its many components, including white blood cells (WBCs), red blood cells (RBCs), and platelets.
A blood centrifuge is also used in the laboratory to separate DNA, which is a key scientific use. In order to do this, DNA samples must first be purified and prepared for separation , and then they must be spun in a centrifuge for a predetermined period of time.
Industrial Uses of Centrifuges
Industrially, they can be used for a variety of applications including water purification, oil separation, protein fractionation and antibody production. In the food industry, centrifuges are used to separate cream from milk.
In the oil and gas industry, centrifuges are essential for separating oil from water and drilling mud. They’re also used to clean up production fluids that contain solid particles like sand or rust.
In addition to their various industrial uses, centrifuges can also be used for research purposes. For example, they are often employed in scientific laboratories where scientists need to quickly and accurately separate different components of a sample. By spinning the sample at a high speed, centrifuges can separate and isolate particles that would otherwise be too small or heavy to be separated by traditional methods.
Centrifuges are a mainstay of industry, used in everything from manufacturing and production to food processing and medicine. But don’t be fooled by their intimidating name, this piece of machinery is surprisingly versatile! Centrifuges can be used for a variety of tasks, making them incredibly useful in the clinical and industrial sector.