In 1978, Louise Brown became the world’s first baby to change state by in vitro fertilization, or IVF. Her birth revolutionized the field of reproductive medicine. As per the latest data, approximately one in eight heterosexual couples has difficulty conceiving. Homosexual couples and single parents often need clinical help to form a baby, the demand for IVF has been growing. IVF is so common, that quite 5 million babies are born through this technology.
In this article specialists from Nisha IVF will discuss how IVF actually works. Nisha IVF is one of the hospitals which provides the best IVF treatment in Ahmedabad. It is a leading hospital in Ahmedabad offering holistic fertility care for the past five years with a well-trained and expert team of gynecologists and fertility specialists. Specialists say that IVF works by mimicking the brilliant design of sexual reproduction.
Natural Process of Baby Making
In order to know IVF, we first got to take a glance at the natural action of baby-making. Believe it or not, it all starts in the brain. Roughly fifteen days before fertilization can happen, the anterior pituitary gland secretes the follicle-stimulating hormone, FSH, which ripens a couple of follicles of the ovary that then release estrogen. Each follicle contains one egg, and on average, just one follicle becomes fully mature. As it grows and continues to release estrogen, this hormone helps coordinate the growth and preparation of the uterus. It also communicates to the brain how well the follicle is developing. When the estrogen level is high enough, the anterior pituitary gland releases a surge of LH, which triggers ovulation and causes the follicle to rupture and release the egg. Once the egg leaves the ovary, it’s directed into the Fallopian tube by the finger-like fimbriae. If the egg isn’t fertilized by sperm within 24 hours, the unfertilized egg will die, and therefore the entire system will reset itself, preparing to make a replacement egg and uterine lining the following month.
Fertilization Process
The egg is that the largest cell of the human body. It is protected by a thick, extracellular shell of sugar and protein which is called the zona. The zona thwarts the entry and fusion of more than one sperm, the littlest cell within the body. It takes a person two to 3 months to form sperm, and therefore the process constantly renews. Each ejaculation during sexual activity releases quite 100 million sperm. But only 100 approximately will ultimately make it to the proximity of the egg, and just one will successfully penetrate through the armor of the zona. Upon successful fertilization, the zygote immediately starts developing into an embryo and takes approximately three days to succeed in the uterus. There, it requires another three approximately days to implant firmly into the endometrium, the inner lining of the uterus. Once implanted, the cells secrete a hormone that signals to the ovulated follicle that there is a pregnancy in the uterus. This helps rescue that follicle, now called the corpus luteum, from degenerating because it normally would neutralize that stage of the cycle. The corpus luteum is liable for producing the progesterone, required to take care of the pregnancy until six to seven weeks of gestation when the placenta develops and takes over until the baby is born about 40 weeks later.
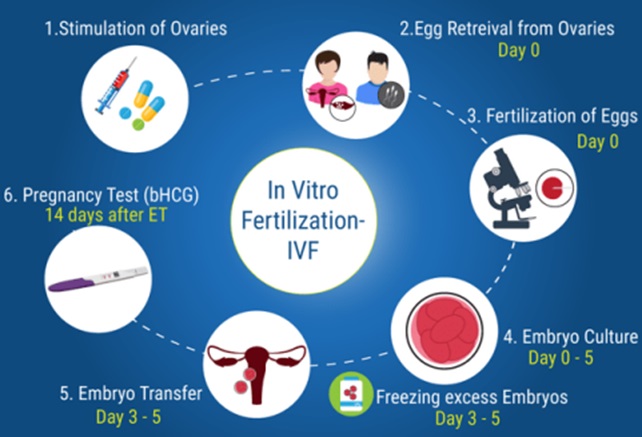
Now, How does one Make a Baby during a Lab?
In patients undergoing IVF, FSH is run at levels that are above present to cause controlled overstimulation of the ovaries in order that they ultimately produce multiple eggs. The eggs are then retrieved just before ovulation would occur, while the lady is under anesthesia, through an aspirating needle that’s guided by ultrasound. In the laboratory, the identified eggs are stripped of their surrounding cells and kept ready for fertilization in a Petri dish. Most sperm samples are produced by masturbation.
Fertilization Process in IVF
Fertilization can occur by one of two techniques. In the first, the eggs are incubated with thousands of sperm and fertilization occurs naturally over a few hours. The second technique maximizes the certainty of fertilization as it uses a needle to place a single sperm precisely inside the egg. This method is more useful when there is a problem with the quality of the sperm. After fertilization, embryos are further screened for any genetic suitability. They are frozen for later attempted pregnancies, or delivered into the woman’s uterus via a catheter. The common process is to transfer the embryo three days after fertilization when the embryo has eight cells. It can be done on day five also when the embryo is called a blastocyst and has hundreds of cells.
Things To Consider
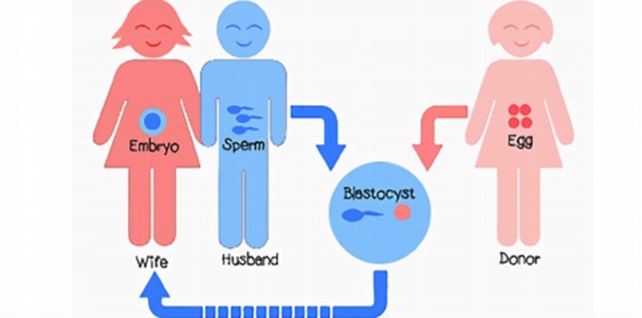
If the woman’s eggs are of poor quality due to age or toxic exposures or have been removed due to cancer, donor eggs should be used to avoid complications. In the case that the intended mother has a problematic uterus, or lacks one, another woman can use her uterus to carry the pregnancy which is known as surrogacy. To increase the chance of success, which is as high as 40% for a woman younger than 35 years, doctors sometimes transfer multiple embryos at the same time. This is why IVF results in twins and triplets more often compared to natural pregnancies. However, most clinics seek to minimize the chances of multiple pregnancies, as they are riskier for mothers and babies.
Final Takeaway
Today millions of babies, like Louise Brown, have been born from IVF and are having normal, healthy lives. So far, IVF seems safe for women. Because of the higher success rate, better genetic
testing delayed childbearing, increased accessibility, and diminishing cost, the day is not so far when artificial baby-making via IVF and related techniques will outpace natural reproduction.