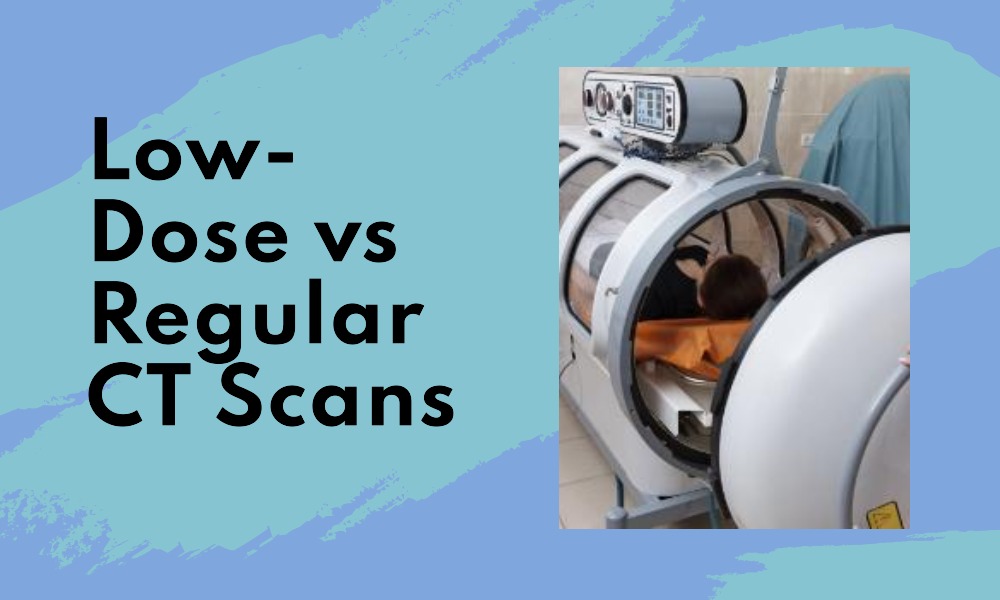
Medical technology has evolved by leaps and bounds, with Computed Tomography (CT) scans at the forefront of diagnostic advancements. CT scans provide clear and detailed images of the body’s internal structures, helping in accurate diagnoses and treatment plans. Two prevalent types are the Low-Dose CT (LDCT) scan and the Regular CT scan. Though they share a fundamental process, there are distinct differences between them. Let’s demystify these differences for a better understanding.
1. The Basics of CT Scans
A CT scan employs X-rays to capture multiple cross-sectional images of the body. These images are then processed by a computer to produce a detailed 3D view of the area being studied. Both LDCT and Regular CT adhere to this principle but differ mainly in the amount of radiation used.
2. Low-Dose CT Scan (LDCT)
- Radiation Level: As the name suggests, LDCT uses significantly less radiation compared to a Regular CT scan, typically around 20-50% less.
- Usage: LDCT is commonly used for routine screenings or high-risk populations where regular monitoring is needed, such as lung cancer screening in heavy smokers.
- Image Clarity: While LDCT offers commendable clarity, the reduced radiation might result in slightly grainier images compared to a Regular CT scan. Yet, for many screenings, this resolution is sufficient.
3. Regular CT Scan
- Radiation Level: Uses a higher dose of radiation to produce detailed images.
- Usage: Employed when detailed imaging is essential, like detecting tumors, studying blood vessels, or evaluating trauma injuries.
- Image Clarity: Regular CT scans offer superior image quality, capturing fine details with greater contrast.
4. Benefits & Limitations
- LDCT Benefits: Reduced radiation exposure makes it safer for frequent screenings. It’s also efficient for detecting abnormalities in specific cases, like nodules in lungs.
- LDCT Limitations: Slightly compromised image quality might not be suitable for all diagnostic needs. There’s also a higher chance of false positives.
- Regular CT Benefits: Exceptional image quality aids accurate diagnoses. It’s versatile, aiding various medical investigations.
- Regular CT Limitations: Increased radiation exposure may not be ideal for routine screenings.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Is the radiation from LDCT harmful? While LDCT uses reduced radiation, any radiation exposure carries some risk. However, the benefits often outweigh the risks, especially in high-risk populations.
- How should I decide which CT scan to undergo? The choice between LDCT and Regular CT should be made in consultation with a radiologist or physician based on diagnostic needs.
- Are preparation methods different for LDCT and Regular CT? Generally, preparation remains consistent for both types. However, specific instructions might vary based on the area being imaged.
- How long does each scan take? Both scans are relatively quick, often completed within minutes. The exact duration might vary based on the body part being examined.
Conclusion
Both Low-Dose CT scans and Regular CT scans play pivotal roles in medical diagnostics. The primary distinction lies in radiation exposure and image clarity. By understanding their differences, strengths, and limitations, patients and medical professionals can make informed decisions, ensuring accurate diagnoses with minimized risks.