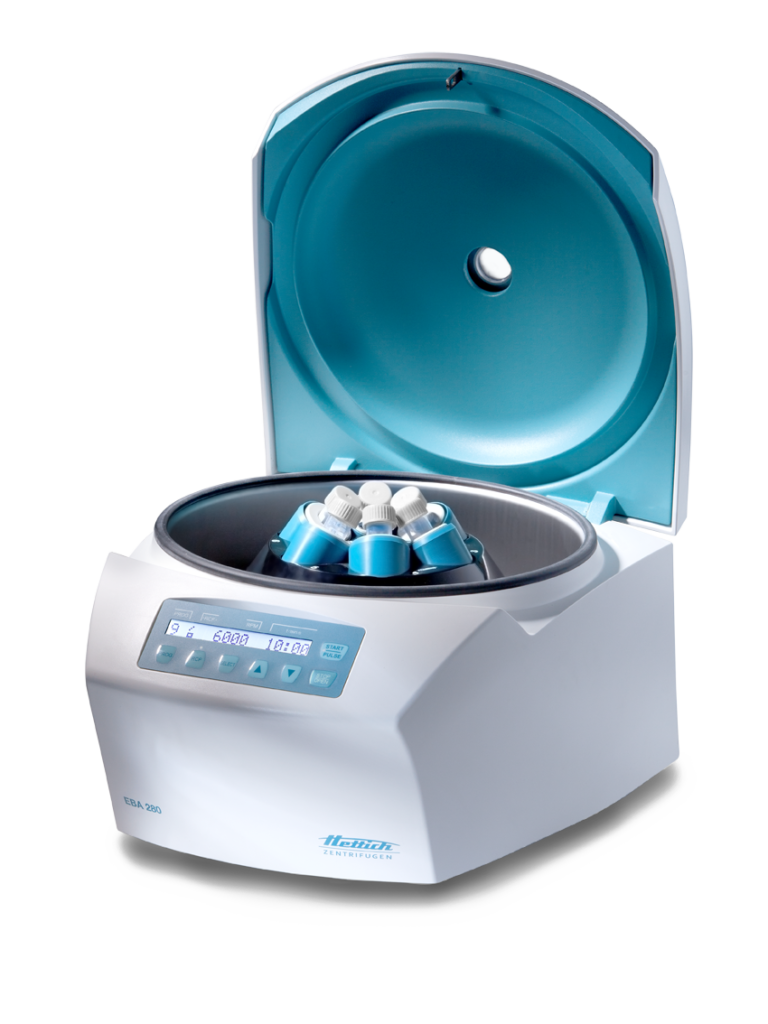
The branch of biology that focuses on the study of diseases and blood serum, especially infectious ones like malaria, AIDS, and hepatitis B is called serology. A serological centrifuge is considered an important equipment and is found in most clinical laboratories.
Serological centrifuges are used to carry out diagnostic tasks and diagnose medical conditions. Serological centrifuges are also used to separate blood cells from the rest of the sample using centrifugal force. It separates blood into other important components.
For instance, serum proteins in the blood that trigger inflammation are separated from the blood component and give more insight into certain conditions. The device can also be used to separate blood plasma from whole blood. This is essential for culturing of bacterial antigens, further processing, and identification of proteins.
How Serological Centrifuges are Used
Whole blood will be placed in the serological centrifuge. This creates a closed system once it is clamped to the surface and securely closed. The rotor of the machine will spin the sample. The cells are pushed outward by the centrifugal force.
As the sample is spun, the centrifuge will create a force that’s proportional to the rate of the spin andthe radius. For clinical work, extremely high forces are not required so small benchtop machines are typically used.
Other Reminders to Keep in Mind
Always make sure you follow the standard safety procedures when using a serological centrifuge. Ensure the centrifuge is placed on a flat and secure position. Always make sure that the sample tube is well balanced and placed securely inside the rotor.
When everything is ready, close the lid of the centrifuge and make sure all the parameters are set correctly before pressing start. Once the run has been completed, carefully open the lid and remove the tubes before turning the centrifuge off.